Affiliate link notice: As an affiliate of BetterHelp and other third-party vendors, We will receive compensation if you make a purchase using the links provided on this page. For more information, visit our disclosure page.
Last Updated on May 27, 2024 by Randy Withers, LCMHC
Pain management is a critical aspect of healthcare, and medications like Percocet play a significant role in providing relief to patients suffering from moderate to severe pain. However, as a potent opioid-based medication, Percocet carries inherent risks that patients must understand and address.
Failure to recognize and mitigate the risks of Percocet use can result in severe consequences, including addiction, overdose, and long-term health complications. This post aims to educate patients about the potential dangers associated with Percocet and offer practical strategies to ensure safe and effective pain management.


Key Takeaways
- Percocet, a combination of oxycodone and acetaminophen, is a potent prescription pain medication that carries significant risks, including addiction, respiratory depression, liver damage, and cognitive impairment.
- Understanding the risks of Percocet use is crucial for patients to ensure safe and effective pain management.
- Following prescribing instructions carefully, maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, and exploring non-opioid pain management strategies can minimize the risks associated with Percocet.
- Individuals struggling with Percocet addiction or misuse should seek professional help and support.
- Prioritizing patient safety and well-being should be at the forefront of any pain management strategy involving Percocet or other opioid medications.
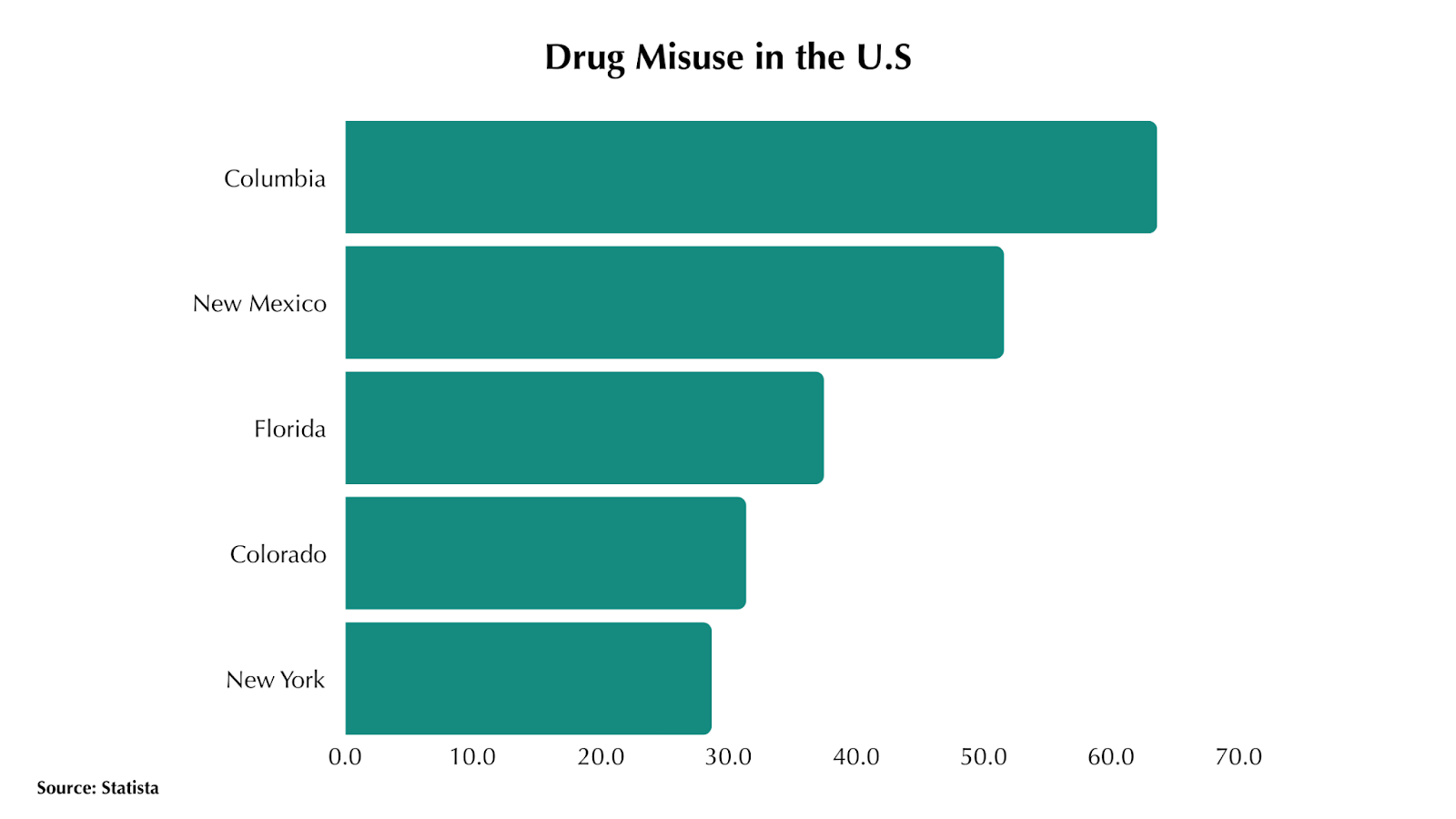
The Opioid Epidemic and Percocet Abuse
The opioid epidemic has ravaged communities across the nation, and Percocet, as an opioid-based medication, has played a significant role in fueling this crisis. While Percocet can provide effective pain relief, its potential for misuse and addiction has led to devastating consequences.
The Staggering Statistics
The opioid epidemic has been a national crisis in the United States, claiming countless lives and devastating families and communities. According to the World Health Organization, nearly 125, 000 people died from opioid-involved overdoses in 2019 alone. Percocet, being an opioid-based medication, carries a significant risk of abuse and addiction, contributing to this alarming epidemic.
The Dangers of Misuse and Addiction
Percocet is intended for short-term use under medical supervision to manage acute pain. However, the potential for misuse and addiction is high, particularly if the medication is taken for an extended period or in higher doses than prescribed.
Opioid addiction can lead to devastating consequences, including job loss, strained relationships, financial difficulties, and even criminal activities to obtain the drug. Referring to Percocet pill identifier guides can help ensure you are taking the correct medication and the correct dosage. It also helps avoid the intake of potential counterfeit medications.
Recognizing Percocet’s Risks
While Percocet can be an effective pain management tool, it is essential to recognize the potential risks associated with its use. Failure to understand and address these risks can have severe consequences, compromising patient safety and well-being.
Respiratory Depression
One of the most significant risks of Percocet use is respiratory depression. Opioids like oxycodone can slow down breathing, and in severe cases, lead to respiratory arrest and death. This risk is particularly heightened when Percocet is combined with other central nervous system depressants, such as alcohol or benzodiazepines.
Liver Damage
Percocet contains acetaminophen, a common over-the-counter pain reliever, and fever reducer. While generally safe when used as directed, excessive or prolonged use of acetaminophen can cause liver damage, potentially leading to liver failure. It is essential to follow dosage instructions and avoid consuming alcohol while taking Percocet, as alcohol can further increase the risk of liver toxicity.
Gastrointestinal Complications
Opioids like oxycodone can disrupt normal digestive processes, leading to constipation, nausea, and vomiting. Prolonged use of Percocet can exacerbate these issues, potentially causing significant discomfort and complications, such as bowel obstructions or impactions.
Cognitive and Motor Impairment
Percocet can impair cognitive function, decision-making abilities, and motor skills. Percocet users may experience drowsiness, dizziness, and confusion, elevating the risk of accidents, falls, and injuries, especially among older adults or individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Minimizing the Risks of Percocet
While Percocet carries inherent risks, patients can employ strategies to minimize these risks and ensure safe and effective pain management. By taking a proactive approach and following best practices, patients can reduce the potential for harm and maximize the benefits of Percocet when used appropriately.
Follow Prescribing Instructions
To minimize the risks of Percocet use, it is essential to follow prescribing instructions carefully. Take the medication exactly as prescribed, and never increase the dosage or frequency without consulting your healthcare provider. Adhering to the prescribed regimen can help prevent adverse effects and reduce the risk of addiction.
Engage in Open Communication
Patients should maintain open and honest communication with their healthcare providers about their pain levels, side effects, and any concerns they may have regarding Percocet use. This transparency can help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about adjusting dosages or exploring alternative treatment options.
Explore Non-Opioid Pain Management Strategies
Patients at high risk of opioid addiction or those experiencing intolerable side effects may find exploring non-opioid pain management strategies beneficial. These may include over-the-counter medications, physical therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, or alternative therapies like acupuncture or massage.
Seek Support for Addiction or Misuse
If you or a loved one is struggling with Percocet addiction or misuse, it is crucial to seek professional help. Support groups, counseling, and medication-assisted treatment can provide the necessary tools and resources to overcome addiction and regain control over one’s life.
| Feature | Percocet | Non-Opioid Medications | Physical Therapy | Alternative Therapies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain Relief | Effective for moderate to severe pain | Effective for mild to moderate pain | Addresses underlying causes of pain | Varying effectiveness based on therapy |
| Addiction Potential | High | Low | None | Low to none |
| Side Effects | Respiratory depression, constipation, cognitive impairment, liver damage | Varies depending on the medication | Minimal | Varies depending on the therapy |
| Long-term Use | Not recommended for long-term use | Generally safe for long-term use | Recommended for long-term pain management | Generally safe for long-term use |
| Monitoring | Requires close medical supervision | Minimal supervision required | Supervised by a physical therapist | Varying levels of supervision required |
| Accessibility | Requires a prescription | Some available over-the-counter | Requires a referral and availability of services | Varying accessibility based on location and costs |
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a vital role in ensuring the safe and appropriate use of Percocet. They must thoroughly evaluate a patient’s medical history, assess pain severity, and consider potential risk factors for misuse or addiction before prescribing.
Responsible prescribing practices include conducting comprehensive assessments, setting clear treatment goals, considering alternative therapies, and providing regular monitoring. Providers must educate patients about risks of Percocet use, including the potential for addiction and dependence, signs of misuse or abuse, the importance of following dosage instructions, safe storage practices, and resources for addiction treatment.
A collaborative care approach involving pain specialists, mental health professionals, and pharmacists can develop comprehensive treatment plans that address patients’ physical, emotional, and social needs.
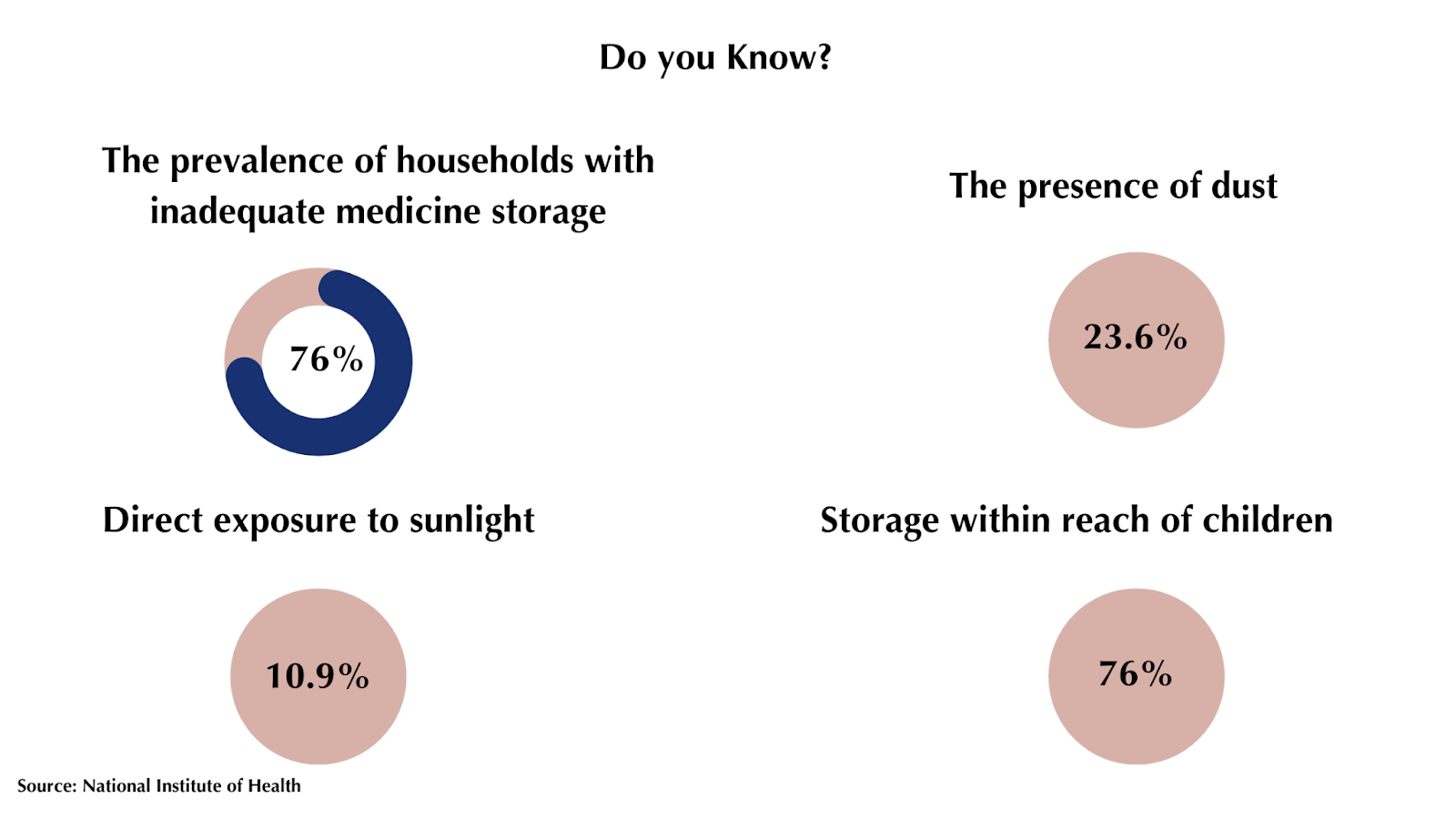
The Importance of Disposal and Proper Storage
Proper disposal and storage of Percocet are critical steps in minimizing the risks of misuse, accidental exposure, and environmental harm. Failure to follow appropriate protocols can contribute to the opioid epidemic and pose serious public health concerns.
When Percocet is no longer needed or has expired, safe disposal methods must be employed to prevent diversion and contamination. Recommended disposal options include utilizing drug take-back programs offered by local law enforcement or pharmacies, using drug disposal pouches or containers that deactivate the medication, or following FDA guidelines for mixing the medication with an unpalatable substance like dirt or used coffee grounds before disposing in household trash.
Flushing or directly discarding unused medications should be avoided. Proper storage is equally crucial to prevent accidental ingestion, especially by children or individuals at risk of misuse or abuse. This involves storing Percocet in its original child-resistant packaging, in a secure, locked location inaccessible to unauthorized individuals.
Storage areas should avoid excessive heat, moisture, or direct sunlight to maintain medication integrity. Regular checks for expiration dates and prompt disposal of expired medications are also advisable. By adhering to proper disposal and storage protocols, patients contribute to mitigating opioid-related risks within their communities.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the risks of Percocet use is crucial for patients to ensure safe and effective pain management. Recognizing the potential for addiction, respiratory depression, liver damage, gastrointestinal complications, and cognitive impairment can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment.
By following prescribing instructions, maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, exploring non-opioid alternatives, and seeking support when needed, patients can minimize the risks and maximize the benefits of Percocet use. Ultimately, prioritizing patient safety and well-being should be at the forefront of any pain management strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the potential side effects of Percocet?
Common side effects of Percocet include respiratory depression, constipation, nausea, drowsiness, confusion, and impaired cognitive function. Long-term use can also lead to liver damage due to the acetaminophen component.
- How can I minimize the risks of Percocet use?
To minimize risks, follow prescribing instructions carefully, maintain open communication with your healthcare provider, explore non-opioid pain management strategies, and seek support if you or a loved one is struggling with addiction or misuse.
- What should I do if I suspect Percocet addiction or misuse?
If you suspect Percocet addiction or misuse, seek professional help immediately. Support groups, counseling, and medication-assisted treatment can provide the necessary resources to overcome addiction and regain control.
Let me know if you liked this post. Your feedback is important!