Traits of circumstances and controls
A complete of 20 sufferers with SCZ and 15 HCs had been recruited for this examine. Amongst these sufferers, 75% had been male, and 25% had been feminine. Whereas 80% had been male, and 20% had been feminine in case of controls. The imply ages of sufferers had been 38.7, in contrast with 39.5 for the management topics. No statistically vital variations had been discovered within the case of age, gender, and physique mass index (BMI) between the circumstances and controls (p > 0.05). All of the SCZ sufferers had been present process an antipsychotic therapy, however that they had not taken any antibiotics or probiotics inside 1 month earlier than sampling.
Sufferers with SCZ exhibit decrease intestine bacterial variety
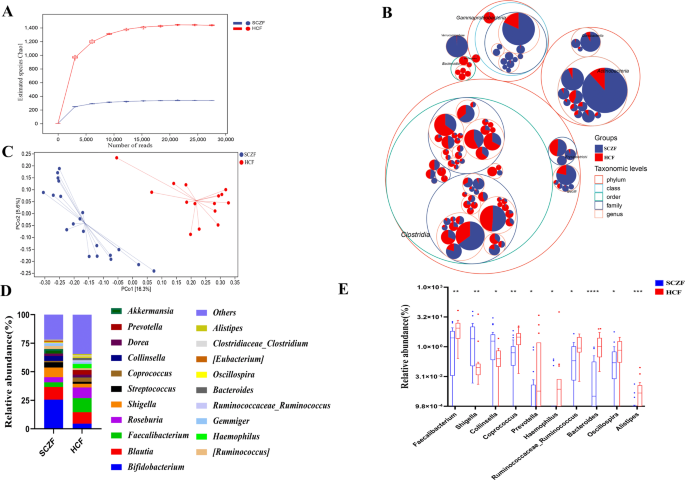
On common, we obtained 43572 high-quality non-singleton reads/pattern. Rarefaction evaluation of the samples confirmed that ASV richness in every group approached saturation (Fig. 1A), and it was considerably decreased within the SCZF group versus HCF group. As estimated by six completely different indexes, intestine microbial variety was considerably decreased within the SCZF versus HCF (p < 0.001; Fig. S1A and Desk S2). Taxonomic tree in packed circles illustrating the general abundance of taxa at completely different ranges, revealed distinct variations within the abundance and distribution of taxa between SCZF and HCF (Fig. 1B). Principal coordinate evaluation (PCoA) evaluation was carried out to show the beta variety, and the outcomes confirmed a major distinction of intestine microbial communities between each teams (Fig. 1C). A Venn diagram revealed that 774 ASVs had been shared between each teams, 2860 ASVs had been sole to SCZF group (Fig. S1B). These findings urged that the intestine microbial group of sufferers with SCZ was characterised by decrease variety.
A Rarefaction curve evaluating SCZF (n = 20) and HCF (n = 15). B Taxonomic variations had been primarily based on 16S rRNA sequencing. Taxonomic composition was visualized by round packing. The most important circles signify phylum, and the inside circles signify class, household, and genus, respectively. The circle sizes signify the imply relative abundance of the taxa. The taxa had been coloured by pattern teams (pink for HCF and blue for SCF), whereas the world of the group corresponded to the imply relative abundance of the taxa in every group. C PCoA primarily based on unweighted UniFrac measures. D Common compositions and relative abundances of the bacterial group in each teams on the genus stage. E Evaluation of variations on the genus stage between SCZF and HCF. SCZF sufferers with SCZ, HCF wholesome controls. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Sufferers with SCZ characterize intestine microbiota dysbiosis
We additional in contrast the bacterial composition and abundance of the intestine bacterial microbiome between SCZF and HCF. We discovered that the phyla Firmicutes, Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria collectively accounted for 93.4% of sequences on common and had been the three main micro organism each within the SCZF and HCF (Fig. S1C). On the phylum stage, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes and Tenericutes had been considerably decreased, whereas Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria had been considerably elevated within the SCZF, in contrast with HCF (Fig. S1D and Desk S3). On the genus stage, Bifidobacterium, Blautia and Shigella had been primarily dominated in intestine microbiome of sufferers with SCZ, whereas Faecalibacterium, Blautia and Roseburia had been primarily dominated in intestine microbiome of wholesome management (Fig. 1D). In contrast with HCF, solely two genera together with Shigella and Collinsella had been elevated, whereas eight genera together with Faecalibacterium, Coprococcus, Prevotella, Haemophilus, Ruminococcaceae_Ruminococcus, Bacteroides, Oscillospira and Alistipes had been depleted in SCZF (all p < 0.05; Fig. 1E, Desk S4). Amongst them, Faecalibacterium, Coprococcus and Bacteroides are important for producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which exhibit essential anti-inflammatory results within the host’s inflammatory response27. Furthermore, it has been reported that Collinsella and Escherichia-Shigella primarily exhibit pro-inflammatory results in numerous illness28. Subsequently, the lower in SCFAs-producing micro organism and the rise of pro-inflammatory micro organism could also be concerned within the inflammatory response in sufferers with SCZ.
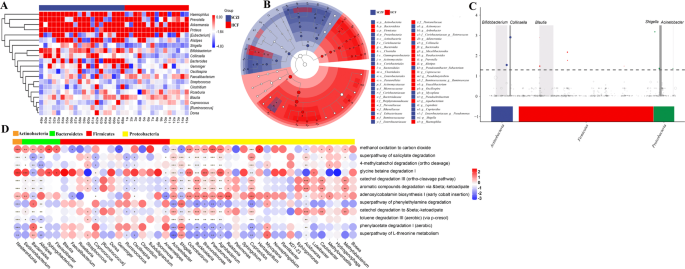
The hierarchical clustering of those modifications in taxon abundance demonstrated distinct clusters of in sufferers with SCZ versus well being topics (Fig. 2A). To find out the variations in intestine microbiota composition and particular taxonomic biomarkers between the SCZF and HCF teams, we additional carried out LEfSe and metagenomeSeq evaluation. LEfSe evaluation confirmed that the relative abundance of bacterial taxa between the 2 teams had vital distinction (Fig. 2B). MetagenomeSeq evaluation confirmed that about 10 ASVs had been considerably enriched in SCZF, and these ASVs primarily belong to Bifidobacterium, Collinsella, Blautia, Shigella, and Acinetobacter on the genus stage (Fig. 2C). Moreover, we analyzed the correlation of predicted differential metabolism pathway and intestine micro organism, and outcomes confirmed that twelve metabolism pathways had been considerably related to the relative abundances Nesterenkonia, Bacteroides, Acinetobacter, Shigella, Burkholderia, Brevundimonas, Pseudomonas, Agrobacterium, Cupriavidus, and Acidovorax (Fig. 2D).
A The species composition warmth map was created in keeping with the Euclidean distance. B LEfSe comparability of intestine microbiota between SCZF and HCF teams. Taxonomic cladogram derived from LEfSe evaluation of 16S sequences primarily based on the homogeneous ASV_table utilizing the Wilcoxon rank sum check within the R software program with correction via FDR. C Manhattan plot. The x-axis represents the microbial ASV taxonomy at phylum stage, and the y-axis represents −log10 (adj p worth). Dots and hole dots point out ASVs with and with out vital distinction, respectively. The colour of every marker represents the completely different taxonomic affiliation of the ASVs. D Correlation evaluation between metabolism pathway and intestine microbes. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Fecal transplant from sufferers with SCZ induces SCZ-like behaviors in recipient mice
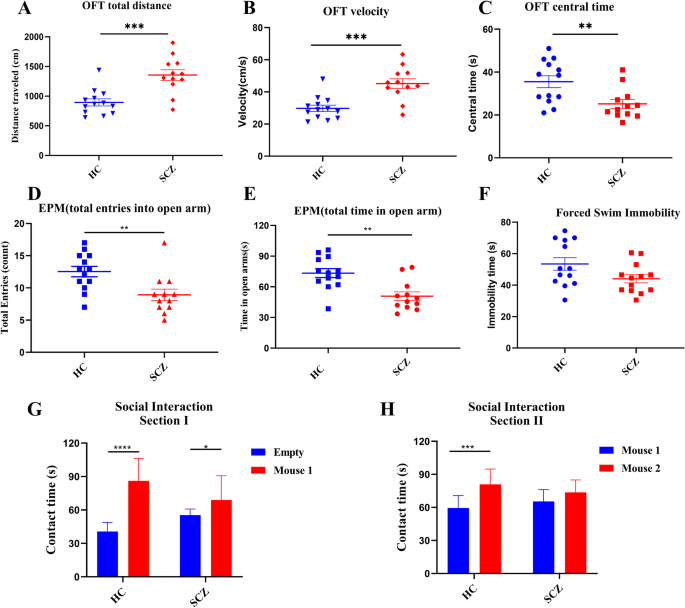
To find out whether or not SCZ-like behavioral signs is likely to be linked with disturbed intestine microbiota, we carried out FMT experiments in SPF mouse. Within the OFT experiment, SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice exhibited hyperkinetic habits (elevated complete distance traveled, Fig. 3A; larger common pace, Fig. 3B), and elevated anxiousness (much less time spent within the heart space, Fig. 3C). Within the EPM check, the variety of entries and time spent within the open arms had been considerably diminished in SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice, in comparison with the fecal microbiota-recipient mice (Fig. 3D, E), suggesting anxiety-like habits. Whereas, there was no distinction between the 2 teams within the compelled swimming check (Fig. 3F). Within the sociability check, HC fecal microbiota-recipient mice spent extra time to discover the chamber inserting a wierd mouse than the empty chamber, whereas this significance of SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient group (p < 0.0001) was considerably decrease than that within the HC fecal microbiota-recipient group (p = 0.0392; Fig. 3G). Equally, HC fecal microbiota-recipient mice spent extra time to discover a novel mouse than a well-recognized mouse, whereas there was no distinction within the time spent to discover a novel and acquainted mouse in SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient group (Fig. 3H). Collectively, these behavioral testing outcomes confirmed that SCZ-like behaviors, together with hyperactivity, elevated anxiousness, impaired social interplay, and reminiscence deficits, had been partially recapitulated in SPF mouse by transplanting intestine microbiota from SCZ sufferers.
A–C Open discipline check. In comparison with HC fecal microbiota-recipient group, each the overall distance traveled (A) and common pace (B) had been considerably elevated, however time spent within the heart space (C) was decreased in SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice. D, E Elevated plus maze check. In comparison with the management group, each the variety of entries (D) and time spent within the open arms (E) had been considerably diminished in SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice. F Immobility time confirmed no vital distinction between two teams. G, H Three-chamber social check. Session I: Totally different from HC-fecal microbiota-recipient mice group, SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice did not exhibit choice for sociability (G) and social novelty (H) (HC, n = 13; SCZ, n = 12). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars stand for the imply ± SD.
Intestine microbiome composition in recipient mice transplanted with SCZ or HC fecal microbiota
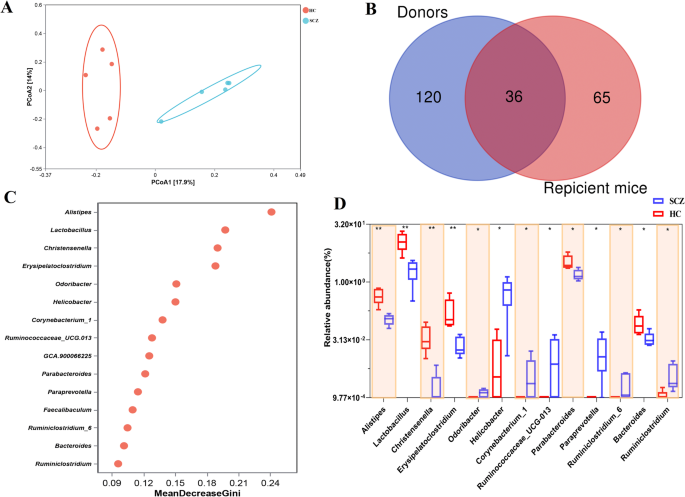
To find out whether or not the same intestine microbial traits of SCZ sufferers had been efficiently recurred within the SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice, we analyzed the intestine microbiota composition of the feces of mice transplanted with SCZ or HC fecal microbiota utilizing 16S rRNA sequencing. The PCoA confirmed an apparent separation between SCZ and HC fecal microbiota-recipient mice (Fig. 4A). A Venn diagram revealed that 36 of 156 genera introduced in donors’ feces had been current within the recipient mice intestine microbiome (Fig. 4B). To determine the featured intestine bacterial microbes that differed between SCZ and HC fecal microbiota-recipient mice, random forest evaluation was carried out. The 15 bacterial genera with the best MDA values had been proven in Fig. 4C. Amongst these, seven genera together with Odoribacter, Helicobacter, Corynebacterium_1, Ruminococcaceae_UCG-013, Paraprevotella, and Ruminiclostridium_6 and Ruminiclostridium had been extra considerable in SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice, whereas the remaining six (Alistipes, Lactobacillus, Christensenella, Erysipelatoclostridium, Parabacteroides, and Bacteroides) had been enriched in HC fecal microbiota-recipient mice (Fig. 4D). It’s price mentioning that Alistipes confirmed the same pattern both in SCZ sufferers or SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice, in comparison with the corresponding controls (Figs.1D and 4D). Earlier research have reported Alistipes is concerned in numerous psychological ailments together with SCZ, by producing SCFA, affecting tryptophan and GABA27,29,30. These outcomes additional authorised that the intestine of SPF mice may very well be re-colonized with the fecal microbiota of SCZ sufferers or wholesome controls by FMT, and Alistipes perhaps the important thing genus concerned in SCZ.
A PCoA evaluation at ASVs stage for microbiome of the feces collected from SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice (SCZ) and HC mice (HC), primarily based on unweighted_unifrac measures. B A Venn diagram displaying the overlaps between human donors and human fecal microbiota-recipient mice. C Random forest plot displaying the 15 most predictive bacterial genera that differentiate SCZ from HC. D Field plots of relative abundance of predictive bacterial genera and the p worth had been calculated utilizing the Mann Whitney check. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Error bars stand for the imply ± SD.
Dysregulated transcriptional response within the mind of SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice
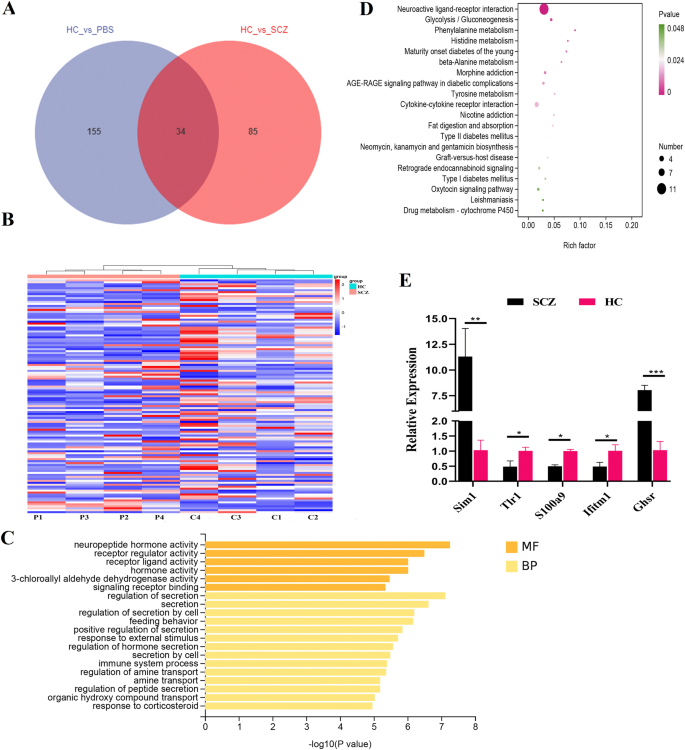
To characterize the molecular mechanisms underlying the behavioral phenotypes in mice transplanted with SCZ fecal microbiota, we carried out RNA-seq of the entire mind samples obtained from SCZ and HC fecal microbiota-recipient mice, and PBS was set automobile management. A Venn diagram revealed that 34 DEGs had been overlapped between SCZ vs HC and HS vs PBS teams, whereas solely 85 DEGs had been sole to SCZ vs HC group (Fig. 5A). Warmth map confirmed a major distinction of the transcripts between SCZ and HC fecal microbiota-recipient mice group (Fig. 5B). As we anticipated, FMT from wholesome human into SPF mice may additionally have an effect on mice mind transcript transcriptome (Fig. S2). To rule out this affect issue, solely these 85 DEGs had been used for GO and KEGG analyses to discover the perform of the DEGs between SCZ and HC microbiota-recipient mice group. The highest 20 GO phrases primarily included neuropeptide hormone exercise, receptor regulator and receptor ligand exercise, immune system course of in mind of SCZ fecal microbiota-recipient mice (Fig. 5C). Bioinformatics analyses urged that the highest 20 enrichment pathways within the recipient mouse mind primarily included Neuroactive ligand-receptor interplay, Phenylalanine metabolism and Histidine metabolism and Cytokine-cytokine receptor interplay (Fig. 5D and Desk S5). Moreover, 5 DEGs had been randomly chosen for additional validation utilizing qRT-PCR, and the outcomes had been in keeping with the RNA-seq knowledge (Fig. 5E).
A A Venn diagram displaying the overlaps between completely different teams. B Heatmap displayed hierarchical cluster evaluation knowledge for 85 DEGs within the mind of mouse from completely different teams. Prime 20 enriched GO time period assignments (C) and prime 20 KEGG pathways (D) for DEGs between two group. E Additional validation of the RNA-seq knowledge through the use of qRT-PCR. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars stand for the imply ± SD.
Overlaps and distinctions of transcriptomes within the brains of SCZ sufferers and fecal microbiota-recipient mice
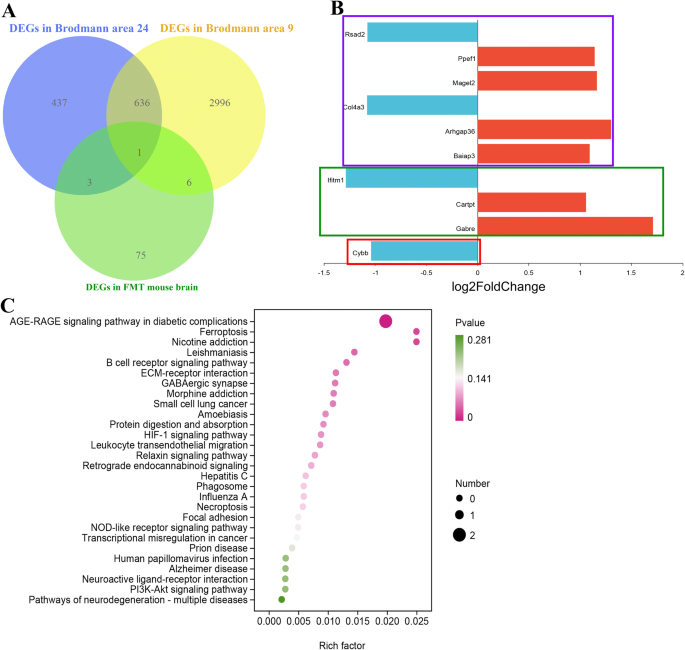
To match transcriptional options and hyperlink the affiliation between SCZ sufferers and FMT mouse mannequin, we additional carried out bioinformatics evaluation to check the transcriptional dysregulation within the brains of postmortem SCZ sufferers and fecal microbiota-recipient mice. Venn diagram confirmed that 7 overlapped DEGs had been noticed between Brodmann space 9 of SCZ sufferers and fecal microbiota-recipient mice, and 4 overlapped DEGs had been discovered between Brodmann space 24 of SCZ sufferers and fecal microbiota-recipient mice (Fig. 6A). Whereas only one overlapped DEGs had been discovered to be current amongst all these three teams (Fig. 6A). All these differential co-expression genes between completely different two teams included Cybb, Gabre, Cartpt, Ifitm1, Baiap3, Arhgap36, Col4a3, Magel2, Ppef1, and Rsad2 (Fig. 6B and Desk S6). The highest considerably enriched KEGG pathways had been primarily concerned in GABAergic synapse, Ferroptosis, HIF-1 signaling pathway, Neuroactive ligand-receptor interplay and Pathways of neurodegeneration-multiple ailments (Fig. 6C).
Venn diagram (A) and bar chart (B) confirmed 4 overlapped DEGs (Genes within the pink and inexperienced rectangles) between Brodmann space 24 of SCZ sufferers and fecal microbiota-recipient mice, 7 overlapped DEGs (Genes within the pink and purple rectangles) between Brodmann space 9 of SCZ sufferers and fecal microbiota-recipient mice, and 1 overlapped DEGs (Genes within the pink rectangles) each in all of the three teams. C KEGG modules differentially enriched between samples of mind from SCZ sufferers and mice mannequin.
Correlation evaluation of the enriched or depleted microbes in FMT mice with differential genes in brains
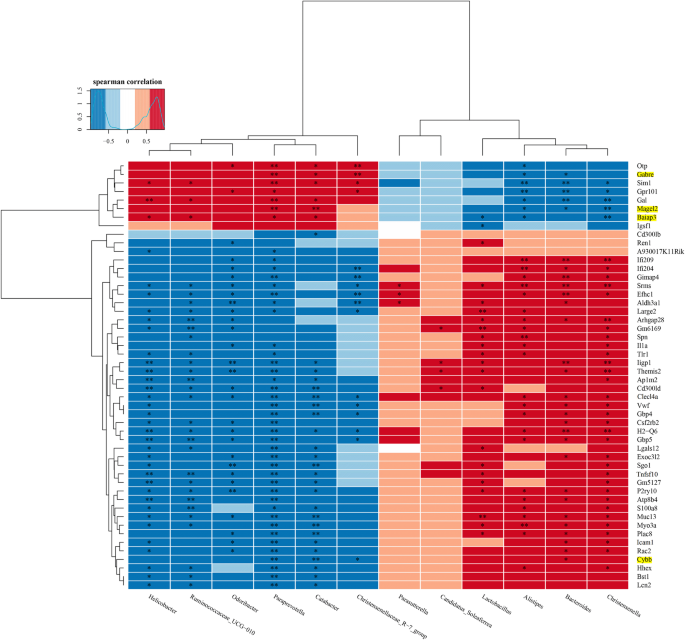
Subsequent, we mixed the FMT mouse microbiome with related mind transcriptomes.
A correlation heatmap was constructed to guage the covariation between altered intestine microbiota genera and altered genes, as proven in Fig. 7. The Spearman’s correlation evaluation confirmed that a lot of the DEGs had been positively correlated with Lactobacillus, Alistipes, Bacteroides and Christensenell, and negatively correlated with Helicobacter, Ruminococcaceae_UCG − 010, Odoribacter, Paraprevotella and Catabacter (Fig. 7). Notably, 4 of the above ten overlapped inflammation-related genes (Fig. 6B), together with Cybb, Gabre, Baiap3 and Magel2 had been recognized to be correlated with the 12 differential genera between two teams of FMT mice (Fig. 7). Curiously, the abundance of Paraprevotella and Catabacter had been all positively correlated with the degrees of Gabre, Baiap3 and Magel2, and negatively correlated with the degrees of Cybb (p < 0.05; Fig. 7). Collectively, the outcomes urged that FMT with intestine microbiota from SCZ sufferers may have an effect on gene expression in mice mannequin. Gabre, Baiap3, Magel2, and Cybb perhaps potential targets for future analysis in SCZ.